🧠 Upside Analysis: Concussion Management and Prevention Ecosystem Analysis: Key Trends, Trends, Drivers, Challenges, Vendors and Recommendations to Pro teams.
Concussion Management and Prevention Ecosystem Analysis
Concussion management and prevention in sports has become a critical focus in recent years due to growing concerns over the long-term impact of repeated head injuries. The increasing awareness of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and other neurological conditions associated with head trauma has led to heightened emphasis on developing tools and strategies for managing and preventing concussions.
This analysis covers the key trends, drivers, challenges, vendors, and recommendations for sports teams involved in concussion management and prevention.
The cost of concussions in the NFL
Quantifying the exact annual cost of concussions to the NFL is challenging due to the multifaceted nature of expenses involved, including medical treatment, player compensation during recovery, litigation, and long-term health settlements. However, several data points provide insight into the financial impact:
Medical Expenses: A study focusing on high school football players reported an average direct medical cost of $800 per concussion. While NFL players likely incur higher medical expenses due to more advanced care, this figure offers a baseline for understanding individual concussion costs.
Concussion Incidence: In the 2021 regular season, there were 187 reported concussions.
Player Compensation: Concussions can lead to significant financial repercussions for players, including a reduction in annual compensation by approximately 7% and a decrease in career length by about one year.
Litigation and Settlements: In 2013, the NFL reached a settlement agreement to provide $765 million for medical assistance to over 18,000 former players affected by neurological conditions, including those resulting from concussions. This settlement underscores the substantial financial liabilities associated with concussion-related health issues.
These figures highlight the significant financial burden concussions impose on the NFL, encompassing immediate medical costs, long-term health care, and legal settlements. While precise annual costs are difficult to ascertain, the cumulative impact is considerable, prompting ongoing efforts to enhance player safety and reduce concussion incidence.
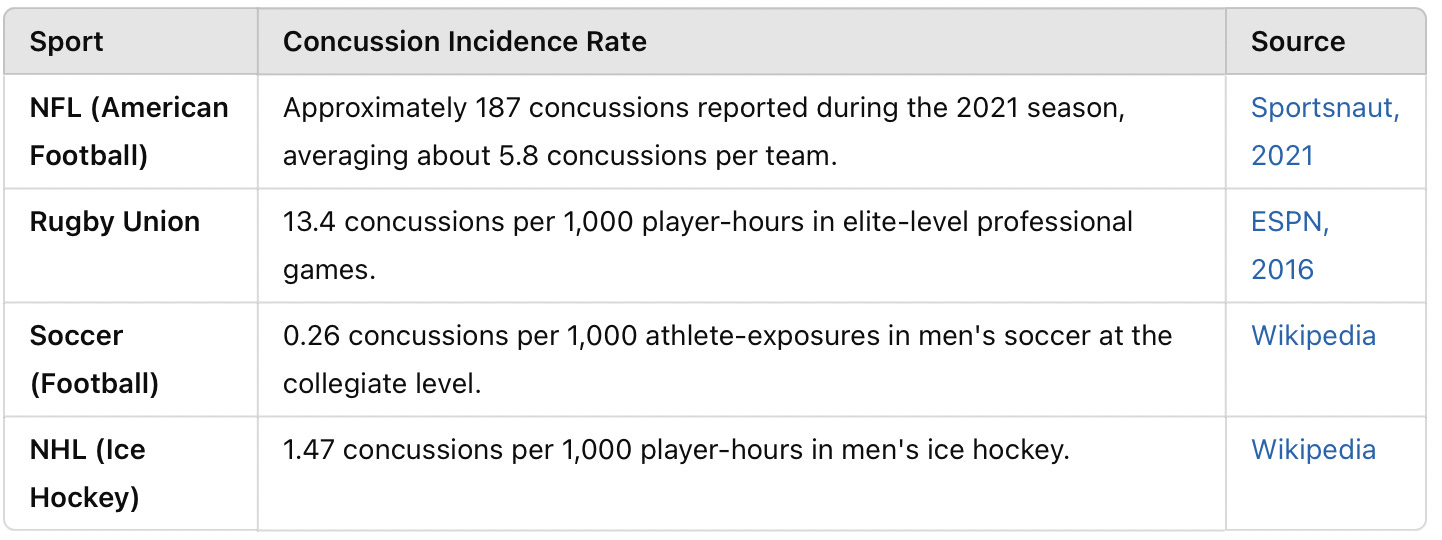
Incidence rates of concussions per sports type (American Football, pro rugby, hockey, soccer)
However, understanding the incidence rates of concussions can provide insight into the potential burden on teams. Below is a summary of concussion incidence rates in different professional sports:
Note: An athlete-exposure is defined as one athlete participating in one game or practice.
While these incidence rates provide a glimpse into the frequency of concussions, the associated costs—including medical expenses, rehabilitation, lost playing time, and potential long-term health implications—vary widely and are not comprehensively documented across all sports. Therefore, specific average cost figures per team are not readily available.
Key Trends in Concussion Management and Prevention
Increased Awareness and Education:
With rising public concern over the long-term effects of concussions (such as CTE), there is a growing emphasis on educating athletes, coaches, parents, and medical staff about concussion risks and symptoms.
High-profile cases of retired athletes suffering from brain injuries have spurred legislation and policy changes aimed at improving concussion management, such as the Return-to-Play (RTP) protocols and Return-to-School (RTS) strategies in youth and professional sports.
Technological Advancements in Detection:
There has been a surge in wearable technology and sensor-based devices designed to detect head impacts and monitor symptoms of concussions. These devices range from mouthguards to headbands and helmet sensors that measure the force of impact and provide real-time data.
AI and machine learning are also being integrated into concussion management systems to predict recovery times, assess brain function, and optimize the Return-to-Play (RTP) process.
Focus on Prevention and Mitigation:
Prevention has become a key area of focus in the ecosystem. This includes innovations in helmet design to absorb impact forces, impact sensors to measure head collisions, and training to teach athletes safer playing techniques (e.g., tackling in football and rugby).
Helmets are being equipped with advanced technology that tracks the intensity and frequency of impacts, allowing teams to better manage athletes’ risk of concussions.
Data-Driven Approach:
Sports teams are using data analytics to monitor and track athletes' head impacts and symptoms over time. This data helps to make more informed decisions about player health, recovery timelines, and whether players are fit to return to action.
Integration of Neurocognitive Testing:
Baseline neurocognitive testing (such as the ImPACT test) has become standard practice in many sports. These tests assess an athlete's cognitive function before the season, and they are repeated post-injury to monitor recovery. These tests are being increasingly integrated with wearable sensors to provide a more holistic view of an athlete’s brain health.
Legislation and Standards:
Many regions and sports organizations have enacted concussion protocols, particularly for youth sports, which require baseline testing and specific return-to-play guidelines after a concussion. Legislation is pushing for stricter concussion management policies, making it essential for sports organizations to adopt effective technology solutions.
Key Drivers of Growth in Concussion Management and Prevention
Player Safety:
The growing concern for player safety, particularly among high-impact sports like football, rugby, and hockey, has driven the demand for better concussion detection and prevention technologies.
Long-Term Health Concerns:
Studies linking repeated head injuries to serious neurological conditions like CTE, Parkinson’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s Disease have made concussion management a top priority for leagues, sports organizations, and athletic trainers.
Increased Investment in Sports Tech:
The explosion of investment in sports tech companies has led to a wave of innovative products aimed at improving concussion prevention, detection, and treatment. The market for wearable devices, impact sensors, and AI-based health solutions is growing rapidly.
Regulatory Requirements:
Governments and sports organizations are instituting regulations that mandate concussion management protocols. For example, the NFL, NHL, and FIFA have all implemented stringent concussion protocols to ensure players are properly managed after head injuries.
Public Perception and Advocacy:
Advocacy groups, such as the Brain Injury Association of America and The Concussion Legacy Foundation, have been instrumental in raising awareness about the dangers of concussions and driving the push for better management practices.
Challenges in Concussion Management and Prevention
Underreporting of Concussions:
Athletes, especially at the youth and amateur levels, may not report concussions due to fear of being sidelined or due to a lack of awareness of symptoms. This makes effective detection and management more difficult.
Limitations of Current Technology:
While concussion detection technology has improved, there is still no perfect solution. Current sensors cannot fully predict the likelihood of a concussion from an impact or assess the severity of a concussion immediately after it occurs.
Some wearable devices can only track the force of an impact but do not measure brain function or cognitive symptoms, which are crucial for a complete diagnosis.
Standardization of Protocols:
While concussion management protocols are widely adopted, there is still a lack of universal standards across different leagues, countries, and levels of play. Variations in protocols can create confusion and inconsistent care for athletes.
Cost of Implementation:
Many concussion management technologies, such as advanced helmets and impact sensors, can be prohibitively expensive for amateur sports teams, schools, or smaller organizations. This can limit widespread adoption.
Long-Term Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Concussions can have varied and long-lasting effects. Managing a player’s return-to-play (RTP) and rehabilitation can be complex, as recovery times vary greatly between individuals, and there is a risk of second-impact syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
Key Vendors in Concussion Management and Prevention Ecosystem
Comparison of Key Vendors by Features and Pricing
Picture: Kinmetrix Arc, 2024
Picture: TopSpin360 helmet, 2024
Pictures: i1 Biometrics, Prevent Biometrics, 2024
Pictures: HEADCHECK Health, 2024
Picture: ImPACT, 2024
Vendor Summary
i1 Biometrics: Offers a smart mouthguard that tracks head impacts and provides real-time data on the severity of those impacts, useful for monitoring concussion risk.
CATASTROPHIC (HEADS-UP): Focuses on concussion prevention and education. Provides concussion awareness and management programs, especially valuable for youth sports.
X2 Biosystems: Provides wearable impact sensors that monitor head impacts during sports activities. Great for tracking head impact data for concussion management.
ImPACT Applications: Offers a neurocognitive testing platform widely used for concussion management. It helps track cognitive recovery post-injury and assesses an athlete’s readiness to return to play.
Brain Sentry: A helmet-based impact sensor system that detects severe impacts and sends real-time alerts to medical staff. Ideal for youth and professional teams.
HeadImpact: Provides wearable head impact sensors that measure force, frequency, and location of head impacts, helping to monitor concussion risks.
SafeHead: A smart cap that monitors head impacts in real-time and sends alerts to coaches and medical teams. It also tracks recovery status.
HEADCHECK Health: provides a mobile and web-based platform for managing concussion protocols, ensuring compliance, and supporting athlete safety through streamlined tracking and reporting.
Kinmetrix: A neck strengthening device designed to reduce concussion risk by improving neck stability. It uses resistance training to build neck muscle strength. It provides advanced neck strengthening technology with data analytics and baseline tracking.
TopSpin: A neck strengthening technology using resistance to improve neck strength and stability, which can reduce concussion risk by preventing head movement during impacts.
Recommendations for Teams
Implement Comprehensive Concussion Prevention and Monitoring Programs:
Teams should adopt a multi-faceted approach to concussion prevention, including impact sensors (e.g., X2 Biosystems, i1 Biometrics, Brain Sentry) and neck strengthening devices (e.g., Kinmetrix, TopSpin), to reduce the risk of concussions and better track athlete safety.
Incorporate Baseline Neurocognitive Testing:
Use ImPACT to establish baseline cognitive functions at the start of the season and track recovery during the post-concussion phase. This is essential for ensuring players return to action safely.
Focus on Youth Sports:
Given the increasing concern about concussion risks in youth sports, tools like CATASTROPHIC (HEADS-UP) can be crucial in raising awareness and improving concussion protocols at the grassroots level.
Track Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Consider investing in recovery tracking systems (such as SafeHead) that monitor head impacts and track recovery status over time, ensuring players are fully healed before returning to play.
Prioritize Neck Strengthening Programs:
Adding neck strengthening routines (via Kinmetrix or TopSpin) to training regimens will help mitigate concussion risks by improving neck stability and muscle strength, reducing the force transferred to the brain during impacts.
Adopt technology that can collect data around the athlete’s neck accurately and show evidence of the progress:
Adopt technologies (e.g. Kinmetrix) that can accurately track data around the athlete’s neck to establish the baseline for each athlete, understand the areas of strengths and weaknesses in the neck, and track how the neck’s strength of an athlete is improving over time.
Adopt concussion management and prevention devices that are safe for the athletes:
Adopt technologies (e.g. Kinmetrix) that can safely strengthen the athlete’s neck in a controlled manner via advanced sensors and robotics. This will go a long way. Avoid using devices that might negatively impact the athlete’s neck in the long run.
Bottom line: In the last few years we have seen the emergence of a large variety of concussion management and prevention solutions. As a result of that, teams have a lot options to choose from. We believe that teams should adopt a fully integrated approach by integrating baseline neurocognitive testing, with neck strengthening and recovery/rehabilitation programs capable of collecting data and evidence of recovery. At the end of the day, by integrating these technologies into a holistic concussion management and prevention strategy, teams can not only protect athletes but also enhance long-term player health and safety.
Of note, this is our last post of the year at Upside so we would like to wish a merry christmas and happy new year to all of you, including our Upside newsletter readers, our customers and partners. Thank you for your continued support! See you all in 2025!
Best,
You may also like: