⭐ Upside Analysis: Motion Capture vs. Markerless Solutions in Elite Sports: A Comprehensive Analysis
In elite sports, success often depends on millimeter-level improvements in technique, efficiency, and injury prevention. Athletes, coaches, and performance staff increasingly rely on biomechanical analysis to gain a competitive edge. Advanced motion analysis enables practitioners to evaluate joint mechanics, movement patterns, and load distribution, informing both training and rehabilitation strategies.
Two primary technologies dominate the field: traditional motion capture (MoCap) systems, which use markers and controlled lab environments to deliver highly precise data, and markerless motion capture solutions, which use computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) to track athletes’ movements without physical markers.
While motion capture remains the gold standard for accuracy, markerless solutions offer practicality, scalability, and real-world usability, particularly for team sports or outdoor environments. Understanding their respective advantages, limitations, and applications is essential for sports organizations aiming to make data-driven decisions that enhance athlete performance while minimizing injury risk.
Definitions
1. Motion Capture (MoCap)
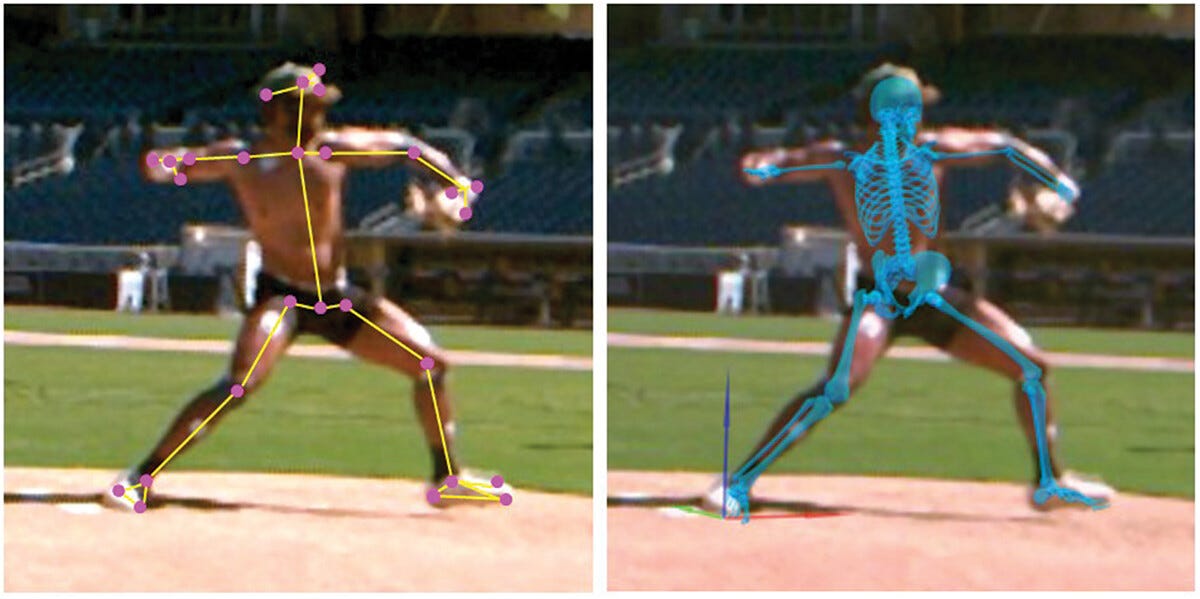
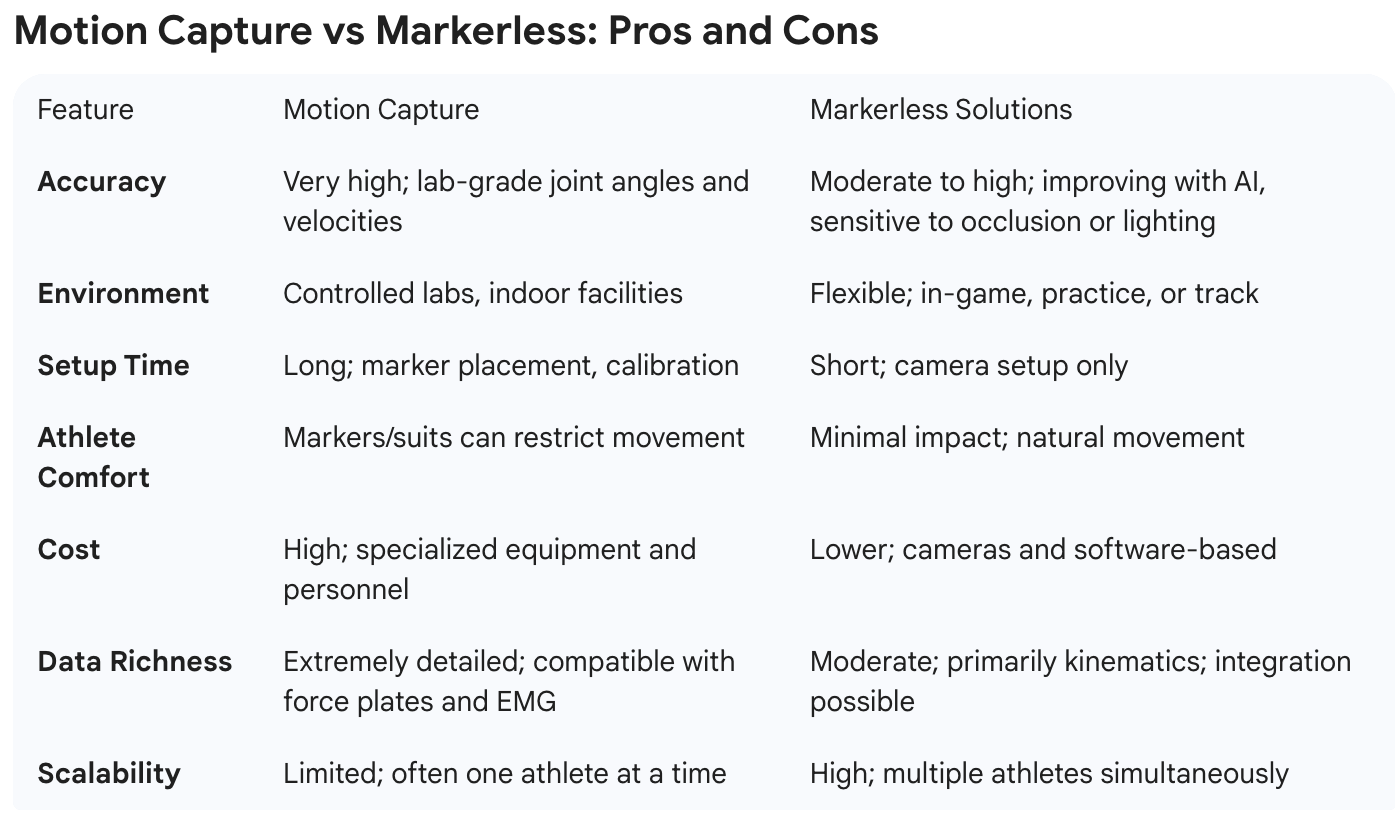
Motion capture involves the use of cameras and sensors to record human movement in three dimensions. Traditional MoCap systems are marker-based, relying on reflective or active markers placed on the athlete’s body, which are tracked by multiple high-speed cameras. This technology captures highly detailed kinematic data, including joint angles, velocities, accelerations, and segment positions.
Key Characteristics:
Requires specialized cameras, markers, and controlled lab environments.
Produces highly precise, lab-grade data suitable for research and elite performance analysis.
Can integrate with force plates, electromyography (EMG), and inertial measurement units (IMUs) for a comprehensive biomechanical assessment.
Often used for injury risk assessment, technique refinement, and rehabilitation monitoring.
2. Markerless Solutions
Markerless systems utilize computer vision, depth cameras, and AI algorithms to reconstruct 3D human motion from video streams or multi-camera setups. They eliminate the need for markers, allowing athletes to move naturally in real-world environments, such as practice fields, courts, or tracks.
Key Characteristics:
No markers or suits; minimal disruption to movement.
Can be deployed in-field, on playing surfaces or tracks.
AI algorithms estimate joint positions and trajectories in 3D space.
Typically more accessible, cost-effective, and scalable, although accuracy may vary depending on environmental conditions.
Motion Capture vs Markerless: Pros and Cons
Source: Upside Global. Confidential, 2026
Key Stats
🔹 Accuracy Comparisons (Joint Angles & Kinematics)
A comparative study of marker‑based and markerless systems during a basketball throwing task found joint angle differences (RMSD) ranged from ~7.2° to ~26.7°, depending on the joint and software version — with newer markerless algorithm versions reducing error and capturing ~93.8 % of the elbow flexion data relative to marker‑based measures. (Source: MDPI)
In multi‑movement testing (including walking and exercise movements), markerless systems showed high correlation with marker‑based systems for lower limb kinematics (e.g., R ≥ 0.877, RMSD ≤ ~5.9°), especially at the ankle and knee, though hip measures exhibited somewhat larger deviations. Source: PubMed),
Main Use Cases in Elite Sports
Motion Capture (Marker-Based)
Technique optimization (pitching mechanics, sprint gait, swimming stroke efficiency)
Injury risk assessment (asymmetry detection, joint loading analysis)
Rehabilitation monitoring (post-surgery recovery, ACL or hamstring rehab)
Biomechanical research and performance modeling
Markerless Solutions
In-game performance tracking (soccer, basketball, rugby)
Team-wide monitoring during practice or matches
Load management and pre-season screening
Player tracking for tactical and technical analysis
When to Use Motion Capture vs Markerless Solutions
Motion Capture is Best When:
Maximum accuracy is required for research or technique refinement.
Detailed joint-level biomechanics are needed for rehabilitation or injury prevention studies.
Working with small groups in controlled environments.
Markerless Solutions are Best When:
Real-world or on-field analysis is required (team sports, track events).
Monitoring multiple athletes simultaneously is a priority.
Athletes’ natural movement must not be disrupted.
Budget, time, or setup constraints exist.
Rationale:
Motion capture offers unparalleled precision but is constrained by cost, complexity, and environmental limitations. Markerless solutions trade some accuracy for scalability, practicality, and real-world applicability, making them ideal for team sports and continuous monitoring.
Future Trends
Hybrid Systems: Combining markerless AI with selective markers or IMUs for enhanced accuracy in real-world settings.
Real-Time Analytics: Instant biomechanical feedback during practice or competition.
Integration with Wearables: Combining heart rate, GPS, and force sensors with motion tracking for holistic performance insights.
AI-Based Injury Prediction: Detecting subtle movement deviations predictive of injury risk.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Scalable storage and remote analysis for teams worldwide.
Conclusion
Both motion capture and markerless solutions are essential tools in modern elite sports. Motion capture remains the gold standard for lab-grade precision, ideal for research, rehabilitation, and technique optimization. Markerless solutions, however, enable practical, scalable, and increasingly accurate monitoring in real-world settings, making them invaluable for team sports, load management, and continuous athlete monitoring.
The future lies in hybrid approaches, combining the precision of MoCap with the accessibility of markerless systems. By strategically selecting and integrating these technologies, sports organizations can enhance performance, minimize injury risk, and gain a data-driven competitive edge.
You may also like:
📈 Upside Analysis: Markerless Systems and Computer Vision in Elite Sports: Key Trends, Drivers, Challenges, Vendors, Recommendations to Teams
Movement analysis is an essential component of elite sports, enabling teams, coaches, and athletes to gain insights into performance, injury prevention, rehabilitation, and tactical planning. Traditional motion capture systems required physical markers and specialized environments, limiting their application in real-world sports scenarios. However, adva…