This week we have the honor to interview Athanase Kollias, and Christos Chalitsios, at KINVENT, a company that helps sports and rehab professionals assess progress and build engagement and motivation. Athanase is the CEO of KINVENT, and Christos is the head of science there. KINVENT is introducing the K-Myo its first EMG product measuring muscle activity so we thought it would be a good idea to bring back Athanase on our podcast along with Christos to talk about this new product.
As a reminder, KINVENT, which was founded in 2017, is a leading player in the fields of physical rehabilitation and sports biomechanics producing innovative measuring and training devices for the facilitation of every day and athletic movements. The company currently has 80 employees and has raised $8M to date. Half is from VCs in France and Greece. The other half comes from business angels coming from sports and rehabilitation. Of note, Raphaël Varane, who is a defender on the French national soccer team, 2018 World Cup Champion, and current Manchester United player, is one of their investors. KINVENT is doing very well financially as it is tripling its revenues every year, and they are looking at $15M-$20M in revenue this year.
KINVENT offers an app, KINVENT PHYSIO, a range of 8 connected sensors measuring strength, muscle fatigue, balance and range of motion of athletes. KINVENT solution helps fasten teams’ rehab process, and assess athletes in one minute. What is also unique about the KINVENT PHYSIO app is that it can understands the baseline of each individuals and uses data from 200,000 patients globally to compare individual data against similar demographics.
Picture: KINVENT sensors in 1 ecosystem
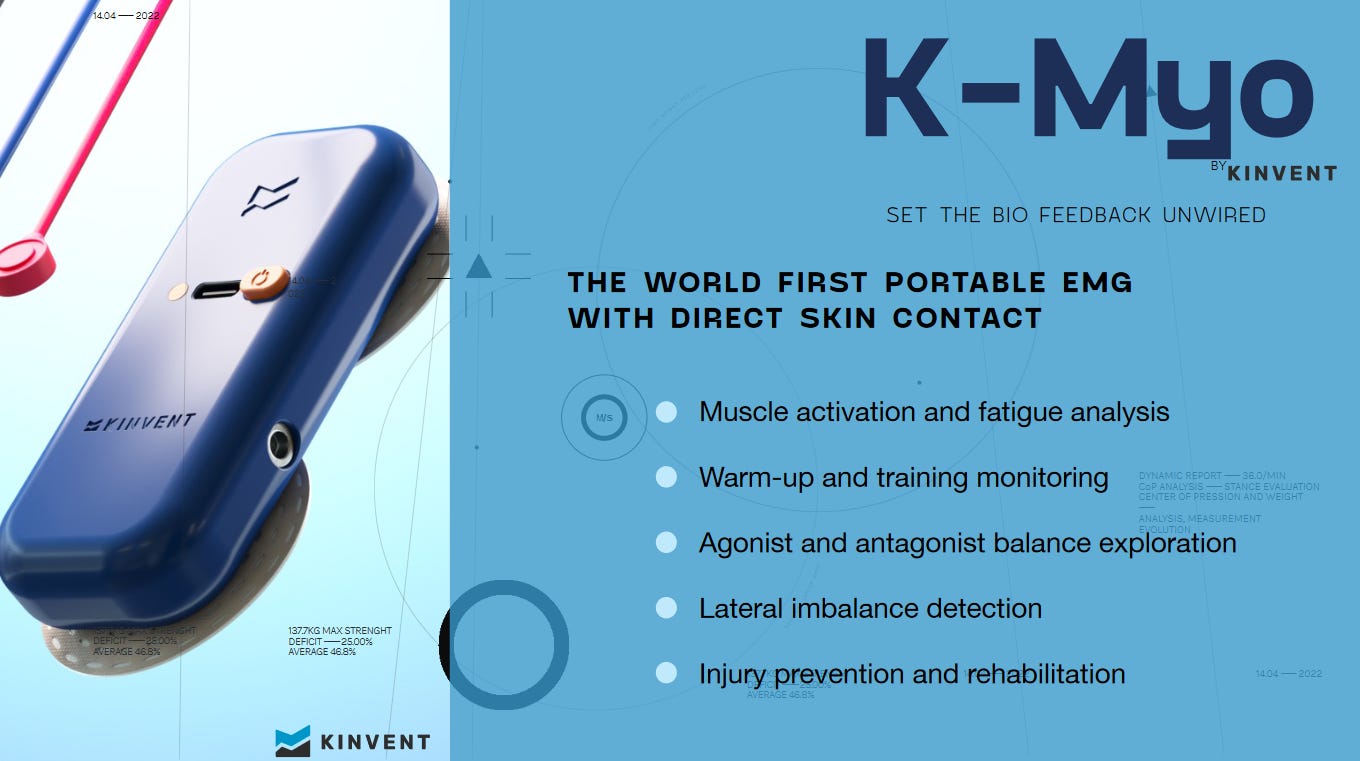
The K-Myo is a portable EMG product with direct skin contact. It enables teams to conduct muscle activation and fatigue analysis. It also helps monitor warm-up and training, agonist and antagonist balance, and detect lateral imbalance. It is also used to help reduce athletes’ injuries and improve the rehab process.
As shown in the picture below, the K-Myo can measure metrics such as asymmetries, activation, muscle fatigue, power and much more.
Here is a video showcasing the K-Myo in action:
As a reminder, their products are currently used globally by 11,000 coaches and physios, and 200,000 patients in more than 57 countries. KINVENT has also built the world’s biggest database of grip assessments as they have collected between 50,000 and 70,000 grip assessments. As shown in the picture below, many other elite teams such as PSG, the Brazilian national soccer team, the French national soccer team, SD Padres (MLB), Houston Dynamo (MLS), Houston Texas (NFL), UFC, INSEP, just to name a few, are using their product today.
Picture: KINVENT’s select sports customers.
📝Show Notes: Through this interview with Athanase and Christos, we touched on what EMG sensors are, how they work, and the use cases to use them. Then we talked about their EMG sensor the K-Myo and how it works, and how it unique compared to other solutions out there. We also discussed the benefits for teams and athletes to use it.
Best Quotes: Here’s some of the key discussion points and best quotes from our conversation with Athanase and Christos:
On the primary use cases to use EMG sensors:
Christos Chalitsios:
“So the primary purpose of an EMG is to help determine if there is a problem with an athlete or a patient's nerve supply to the muscle or both the Muscle or the nerve. It can pinpoint nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction, or issues with the connection between nerves and muscles”.
“This is useful in diagnosing conditions like muscular dystrophy, nerve compression disorders, or nerve injuries. After significant muscle strains, there are alterations in the stability of the muscles and all of these can be assessed and evaluated with an EMG. So if we break it down even further, we can say that EMG is a tool to gauge the health of our own functionality of muscles, or detect muscle activity or muscle overactivity because it's pathology to have inactivity or overactivity”.
“There is a sweet spot between muscles, muscle activation, then biofeedback and rehabilitation, especially for athletes or individual undergoing physical therapy. EMG is used as a biofeedback tool most of the time by visualizing the electrical activity of muscles in real time. Patients can learn to activate specific muscle more efficiently”.
“It is especially useful in rehabilitating of, muscle injuries or after surgeries where there is a distortion of muscle activation. Furthermore, we can say that also we can detect and perform a muscle fatigue analysis because fatigue, both chronic or acute also alter muscle activation”.
“And if we can detect that, we can guide training regimens, rest interval, or even give ergonomic advice to everyday people. And of course, another use case is research and muscle physiology. So beyond the clinical and rehabilitative rehabilitative application of an EMG, which is vital, scientists utilize EMG sensors to understand muscle fiber recruitment and recovery and other intricate, let's say aspects of muscle function”.
On why they decided to launch their new EMG product called the K-Mayo:
Athanase Kollias:
“So as CE0 and CTO of KINVENT, to be honest with you, actually up until today, KINVENT was mostly centered on biomechanics. We were mostly centered in measuring the mechanical outcome of a human movement”.
“For example, a guy jumps or does squats, and he's a very powerful squatter. He can take lots of weight on him and he can do it in a very good speed. Now can this guy be even better? So this is where we will get in with an EMG and try to understand the technique he uses. Does he use his quadriceps the same, and his left and right quadriceps at the same time? Does he use his hamstrings also?”.
“Because we can see some patterns and say, okay, there is a smaller activation on the left quadriceps. Let's try to work on that because this guy can get even better, can be even better in his squats. So there is a need in combining biomechanical outcomes with physiological signals. EMG is one of them. And then there are other ones, but that's for the future of KINVENT. So for now, there is a big need in combining both. Now, why we decided to do it now is because people really asked for it”.
“So in the last year or two, we had lots of demands in trying to understand the muscle itself. So that's why we decided to launch this project. And it was 9 or 10 months ago”.
On how the K-Myo works, and how to set it up:
Christos Chalitsios:
“The K-Mayo is a small wireless device, utilizing the Bluetooth connection as all of our devices, and using both dry or wet electrodes. The difference is that the conduction is somewhat different, but you can use both types of electrodes on the muscle that you capture, and connect it to your phone and voila, you have the activation just right on your mobile devices”.
“And what's even better is that you can synchronize it with all of devices that measure force. And you have in a very neat solution all of your signals, all of your data and have the insight just in your mobile device”.
Athanase Kollias:
“The Bluetooth connection is around 20, 25 meters, I think 25 meters when you combine the sensors with others and you can go up to 50 meters in open field”.
On why they decided not to put EMG sensors into a compression short and use a small form factor, and how the K-Myo is unique from other products out there:
Athanase Kollias:
“So there was, for example, a company Prime Wearables or Atlas, they were offering shorts. And actually it seems pretty non-invasive because you just need to put the short on an athlete. And then when we discussed with players, athletes, they actually told us the opposite. They said that they actually don't want to wear other shorts or other shirts”.
“We are also not experts in textile and fabrics (…) The second thing that we saw is that all those kinds of fabrics we had more issues with the connections with wires and with the fabrication itself. They were more expensive, so it was an issue as well”.
“So that's why we went with small solutions. We wanted to do something that is really small and that you just stick on the skin. And how can you take it on the skin? This is where we searched and we found that there are patches that you can use and reuse. And you just put the patches on the electrodes on the EMG. You just stick it to the skin and you have your signal and that's it (…) The K-Myo weights about 60 grams (..) It's the lightest EMG product with two channels. We are able to follow two signals, two muscles at the same time”.
“You could use two K-Myo on two muscles. In the market, with those two signals, our EMG sensor is the lightest and smallest EMG sensor out there”.
On how the K-Myo can be used by teams to help improve athletes’ rehab, technique and track their fatigue:
Athanase Kollias:
“Th K-Mayo can be useful in three areas. First of all, it can be used for rehabilitation. Second it can be used to track fatigue. And third it can be used to improve an athlete’s technique during loading, running, et cetera”.
Christos Chalitsios:
“With an EMG device like the K-Myo, you can understand the sequencing of muscle activation. What you are looking is coordination of complex movements, like a golf swing or a baseball pitch”.
“EMG can help break down these movements, ensuring that its muscle group will fire optimally and in coordination with the others”.
“When it comes to rehab, imagine biofeedback training because for rehabilitation, biofeedback is crucial. EMG can be used like a biofeedback tool providing athletes with the real time feedback of on muscle activation patterns. This will help them learn to activate and coordinate the specific muscular groups effectively”.
“So if you have an injury and a muscle is not activating after a surgery, using an EMG can help athletes reeducate their nervous system to start activating properly the muscle again”.
On which teams are already using the K-Myo:
Athanase Kollias:
“KINVENT is based mainly in France, so our first users are French teams and federations such as the French Rugby Federation, who is currently preparing for the World Cup. Other teams using it are the Montpelier rugby team who were champions in the Top 14 league two years ago. They are currently using it during their preseason”.
“They use it on athletes that had a surgery and also on their main athletes in order to check their techniques. We also sent it to researchers to see how they can use it in their research and how they can validate it”.
“Lots of physios also use it currently in their own clinic, using it mainly with post-surgery patients like ACL hip surgery, hip arthroplasty, knee arthroplasty, shoulder surgeries, et cetera”.
“In the United States, we have already some users at the HSS hospital for special surgeries. The Stanford University and the NY Mets (MLB) are also using the K-Myo”.
On the pricing and business model
Athanase Kollias:
“We wanted to launch 200 units of the Black Edition. And actually we don't have anymore units left. But that's a good problem to have. The K-Mayo will be delivered to the general public starting in September 2023. But we have a big backlog of orders”.
“The K-Myo i not expensive. It's available for 990 euros or $990 to get the main kit. And then there are some accessories that can accompany it. But what we mainly propose is that you combine this with two K-Myo units so that you can follow left and right at the same time together with a pair of force plates and with dynamometers.
On the best way to reach out to Athanase and his team at KINVENT:
Athanase Kollias:
“You can contact us at info@kinvent.com., or on our website, or people can download our app and there is a support button there you can contact our support team”.
You may also like:
🔥Upside Chat: Athanase Kollias, CEO of KINVENT, a Leading Sports and Rehab Professional Assessments Company
🔥 Upside Chat: Dave Hancock, CEO, Apollo (Leading Athlete Management Systems (AMS) vendor)
🔥Upside Chat: Alexi Pianosi, Strengths and Conditioning Coach, Pittsburgh Penguins (NHL)
🔥Upside Chat: Pierre Barrieu, High Performance Director, Toronto FC (MLS)
🔮 2022 Upside Top Sports Tech Predictions (NFT/Metaverse, Sports Performance, IPOs/M&As..)
🔗 🔥 Upside Analysis: NFTs Vs Crypto Vs Digital Currency, How Are They
Different?